Lisbon 1890 (EPSG:4803)
Lisbon 1890 (EPSG:4803) is a regional non-geocentric datum established by Portugal at the end of the 19th century. It primarily provided a unified coordinate framework for the country's early terrestrial surveying and topographic mapping (for example, when combined with the Bonne projection to form EPSG:2963). As a national standard from a specific historical period, it has been completely superseded by modern geocentric datums (e.g., ETRS89). Its current value is limited solely to processing and converting legacy Portuguese data such as historical maps and cadastral archives from the late 19th to mid-20th century, which, after professional conversion, can be used for digital archiving and historical geographic analysis.
2025-12-29 16:45:37Roma40 (Rome 1940, EPSG:4806)
Roma40 (Rome 1940, EPSG:4806) is a regional, historical geodetic datum designed specifically for Italy and its surrounding regions (such as Sicily and Sardinia), and belongs to the geocentric coordinate system. Its core purpose was to provide a benchmark for official Italian surveying from the 1940s to the 1990s.
2025-12-29 16:38:56ED87 (European Datum 1987, EPSG:4231)
ED87 (European Datum 1987, EPSG:4231) is a regional geodetic datum established in 1987 specifically for Europe, primarily Western Europe. It is a traditional geodetic datum designed to align the coordinate framework as closely as possible with the European geoid at the time and served as a key intermediate achievement in the modernization of European geodesy. Its primary application is in processing historical surveying data, topographic maps, and engineering drawings from Western Europe predating the 1990s. However, as a transitional datum based on terrestrial triangulation, its accuracy and global compatibility are now insufficient. Today, it is mainly used for scenarios such as historical data integration, digital archiving, and specialized research after being transformed into modern geocentric coordinate systems like WGS84 or ETRS89.
2025-12-29 16:30:44NAD27 (North American Datum 1927)
NAD27 (North American Datum 1927) is a geodetic datum established in 1927 for North America, defined based on the Clarke 1866 ellipsoid with its origin at Meades Ranch in Kansas, USA. This datum served as the official mapping and surveying standard for the United States, Canada, and Mexico for decades, widely used in historical topographic maps, land ownership records, and traditional geographic data. Although its accuracy is limited by early surveying technology and it has been superseded by more modern datums (e.g., NAD83), a significant number of historical archives and legacy systems still rely on NAD27. Therefore, special attention must be paid to datum transformations when dealing with older geographic data in North America.
2025-12-29 16:04:49Gaia-CRF3 (Gaia Celestial Reference Frame 3)
Gaia-CRF3 (Gaia Celestial Reference Frame 3) is the latest generation of celestial reference frame constructed by the European Space Agency's (ESA) Gaia satellite mission. It primarily uses ultra-distant celestial objects such as distant galaxies and quasars as reference points, providing a highly accurate spatial coordinate reference in space that is unaffected by Earth's motion or rotation. Gaia-CRF3 serves as a foundation for position determination in astronomy and space geodesy, complementing and enhancing the previous ICRF (International Celestial Reference Frame).
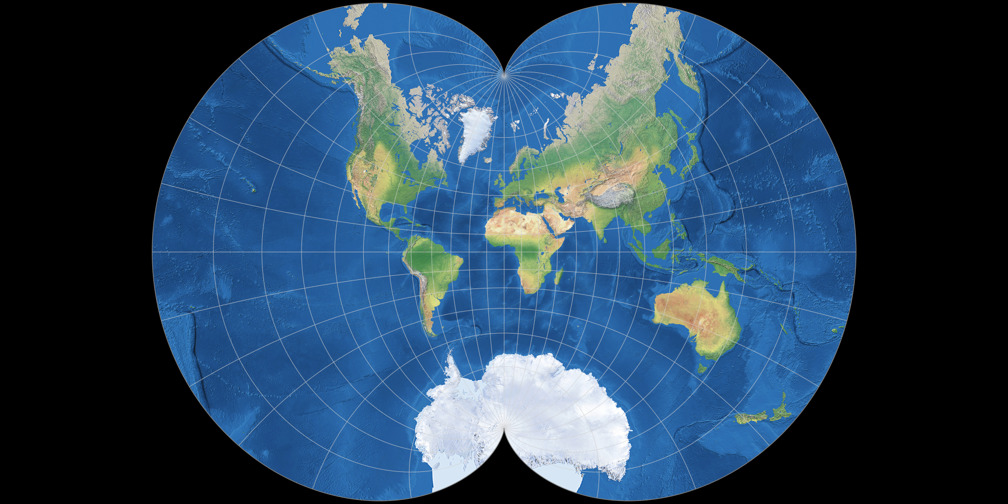
2025-12-29 15:08:37Eckert IV
Eckert IV (Eckert's Fourth Projection) is an equal-area map projection proposed in 1906 by German mathematician Max Eckert. Designed for representing the entire Earth on a world map, it accurately preserves area while distributing shape distortions relatively evenly. It is commonly used in GIS and thematic mapping for visually representing statistical data and distribution information. It is implemented by ESRI as ESRI:54012.
2025-12-29 15:03:20Collignon projection
Collignon projection is a type of equal-area projection (authalic projection) proposed in 1865 by the French mathematician Édouard Collignon. It is designed to represent the entire Earth on a plane, with the key feature of accurately preserving area. It is primarily used for world maps and statistical maps, especially in visualizations that emphasize area comparisons between regions.
2025-12-29 14:56:12Foucault Sinusoidal Projection
Foucalut Sinusoidal Projection is a type of pseudocylindrical projection proposed in the 19th century by the French physicist Léon Foucault. It is based on the sinusoidal projection and is characterized by the introduction of a correction coefficient to adjust distortion in the latitudinal direction. This projection aims to improve shape balance from low to mid-latitudes while maintaining overall equal-area properties, making it suitable for thematic and statistical maps that display the entire world.
2025-12-29 14:49:35August Epicycloidal Projection
August Epicycloidal Projection is a pseudazimuthal world map projection devised by mathematician Ferdinand August in the 19th century. This projection is characterized by the arrangement of meridians and parallels based on epicycloid curves, with the aim of representing the entire world on a single map. While it does not strictly preserve area, angles, or distances, it offers overall visual balance and a unique geometric beauty, making it primarily suitable for theoretical and educational purposes or the study of map projections.
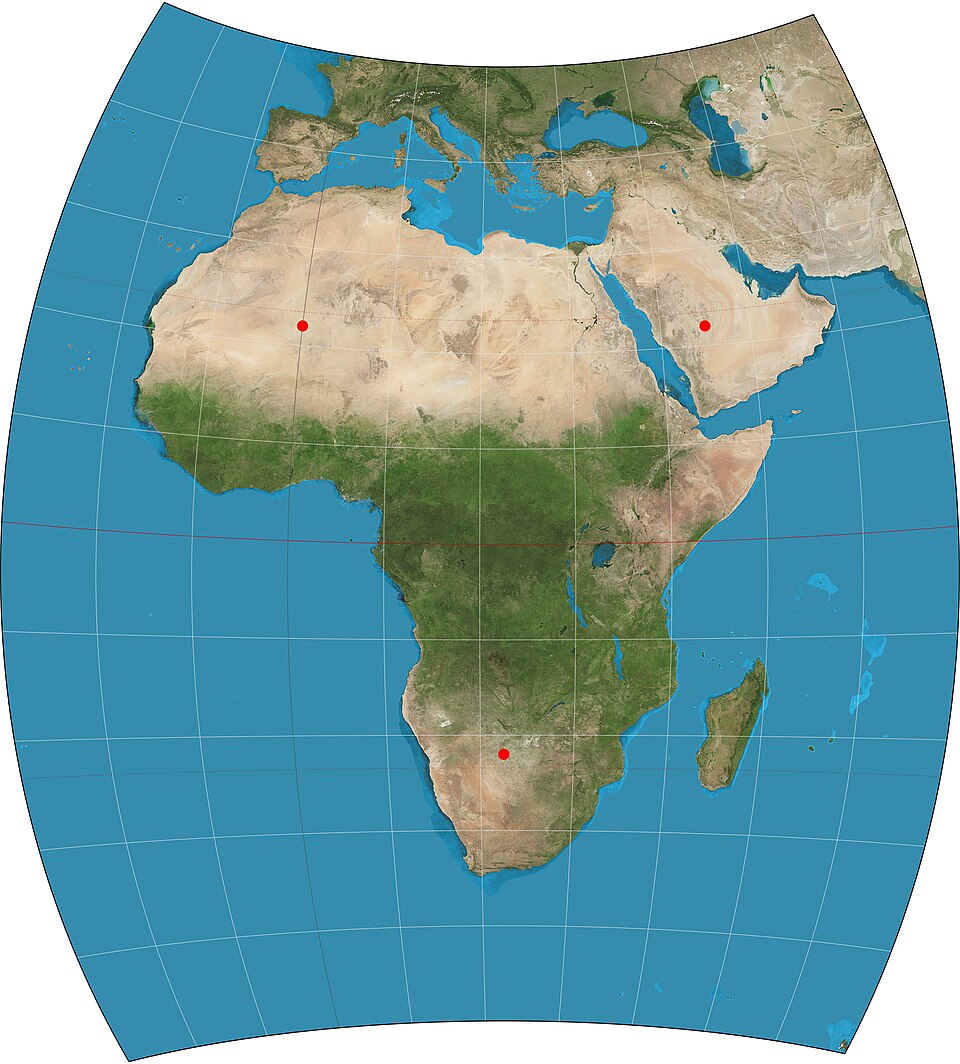
2025-12-29 14:41:13Chamberlin Trimetric Projection
Chamberlin Trimetric Projection is a map projection method devised by William Chamberlin in the early 20th century. This projection is characterized by its accurate preservation of distances from any three arbitrarily chosen points on the Earth's surface. It is classified as a "compromise projection," as it does not fully belong to any of the conformal, equal-area, or equidistant categories. It excels in representing regions centered around specific reference points and has been used for experimental and academic purposes to intuitively understand geographical relationships.
2025-12-29 14:35:59
 Service
Service